Global sleep problems might be causing MORE DAMAGE than terrorism. Sleep on that.
One sleepless night, nothing to worry about, they said. This is what many Americans and people around the world say right before they are in a car crash or make a fatal mistake at work.
We all know that sleep is necessary for our physical and mental health, but very few know how important it really is. The truth is that we take sleep for granted.
Sleep deprivation is similar to alcohol intoxication, and it may be helpful to think of it that way. So, would you go to work intoxicated by alcohol? You certainly would not.
In just 10 minutes, these 54 sleep statistics will make it clear to you that sleeping disorders and deprivation are NO JOKE, and we should all take our sleep more seriously.
Who knows, knowing all this might save your or someone’s life. It also might help you find the best mattress – who knows?
General Sleep Data and Stats
Sleeping 60 to 90 minutes more per night can make you happier and healthier.
REM Sleep constitutes 25% of our total sleep time while the remaining 75% are the non-REM sleep stages.
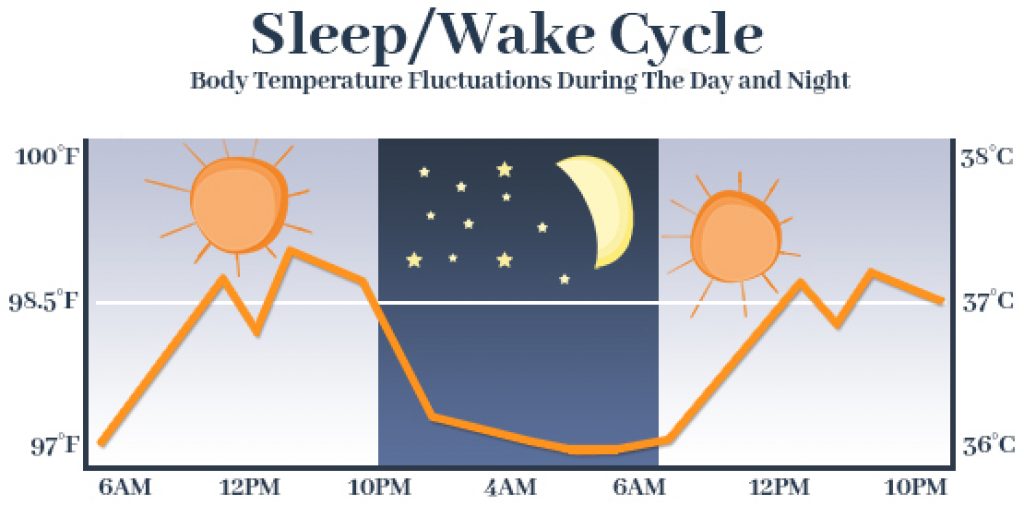
Typically, our body temperature decreases during sleep and increases during the wake phase repeatedly.
54.1% of adults prefer to sleep in the fetal position while 37.5% sleep on their back.
6-8% of the participants in one study reported a condition called “sexsomia” which means engaging in sexual activity during sleep.
Sleep Deprivation Statistics
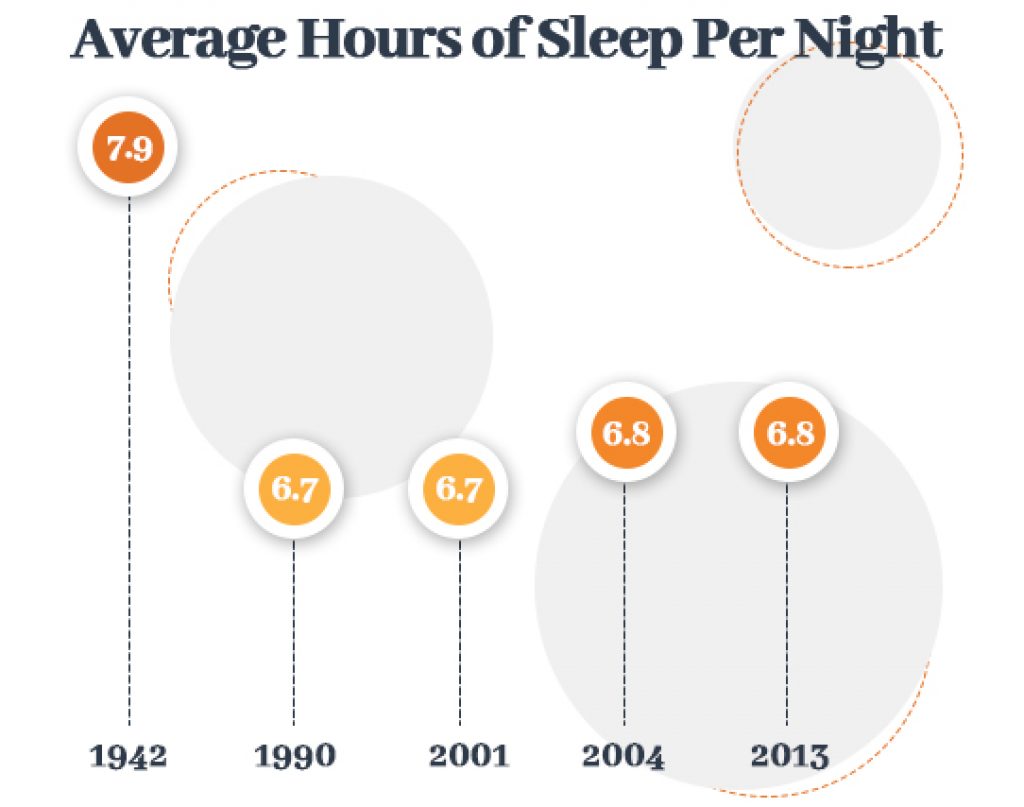
In 1942, Americans had 7.9 hours on average hours per night compared to 6.8 hours in 2013, which is a 13% decrease.
Falling asleep takes on average 10-15 minutes. If you pass out within a few minutes, it might mean you are sleep deprived.
Lack of sleep costs the United States over $411 billion dollars and 1.23 million working days annually.
One in three adults doesn’t get enough sleep.
Age 40 is when Americans get the least amount of sleep.
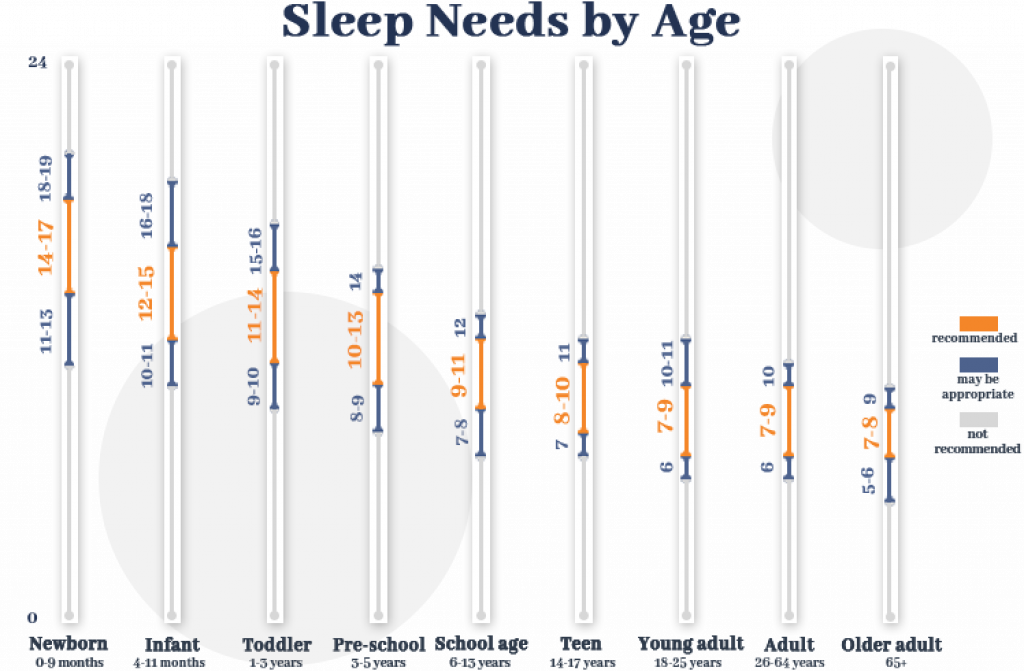
Most teenagers only get about 6.5 to 7.5 hours of sleep per night, although they should sleep between 8 and 10 hours.
Not getting enough sleep may cause problems with learning, reacting, and focusing, making it difficult to make decisions, control your emotions, solve problems, or cope with change.
Sleep deprivation is linked to an increased risk for medical errors by physicians.
People with a college degree or higher have the most sleep (72%), while unemployed or those unable to work much lower (at 51 and 60% respectively).
Healthy Sleep duration is more common among married people (67%), and lower in those who were never married (62%) or who were divorced, separated, or widowed (56%).
37% of people between 20 and 39 years old reported short sleep duration.
Hawaii is the most sleep-deprived state, and Minnesota is the least sleep-deprived state.
Almost 20% of all car crash accidents and injuries are associated with sleepiness.
Sleep deprivation increases your risk of obesity.
Sleep Disorders Statistics
About 70 million people in the U.S. struggle with sleep disorders.
90 million people in the U.S. have reported snoring problems.
Explore the best pillows for snoring.
4.2% reported falling asleep or nodding off while driving in the last 30 days.

Almost 40% of adults report unintentionally falling asleep during the day at least once a month.
Insomnia
30% of U.S adults experience insomnia, and one in ten experience chronic insomnia.
[22] American Medical Association
Check out the best mattresses for insomnia.
People with insomnia have an increased risk of health complications, including diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, stroke, and obesity.
About 50% of insomnia cases result from anxiety, depression, or psychological stress.
Sleep Apnea
Nearly 1 billion adults around the world experience obstructive sleep apnea.
[25] National Library of Medicine
Check out our picks for the best CPAP machine.
12.6% of men and 3.3% of women reported having obstructive sleep apnea.
Men are less likely to report obstructive sleep apnea symptoms but more likely to have the disorder than women.
[26] National Library of Medicine
90% of obstructive sleep apnea cases go undiagnosed.
Over 50% of diagnosed sleep apnea cases are reported in people aged 40 and over.
[28] National Center for Biotechnology Information
Explore the best mattress for sleep apnea.
Narcolepsy
One in 500 people that carry a gene responsible for developing narcolepsy will actually develop the disorder.
[29] National Organization for Rare Disorders
Only 20-25% of people will have all four narcolepsy symptoms (daytime sleepiness, sudden loss of muscle function, sleep paralysis, and hallucinations).
[30] National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
Over 60% of Narcolepsy patients were misdiagnosed as obstructive sleep apnea or depression.
It is estimated that 75% of people suffering from Narcolepsy remain undiagnosed.
[30] National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
Experts estimate that 135,000 to 200,000 Americans have narcolepsy.
135,000 to 200,000 people in the United States have narcolepsy and affects men and women equally.
[30] National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
Sleep Aids Statistics
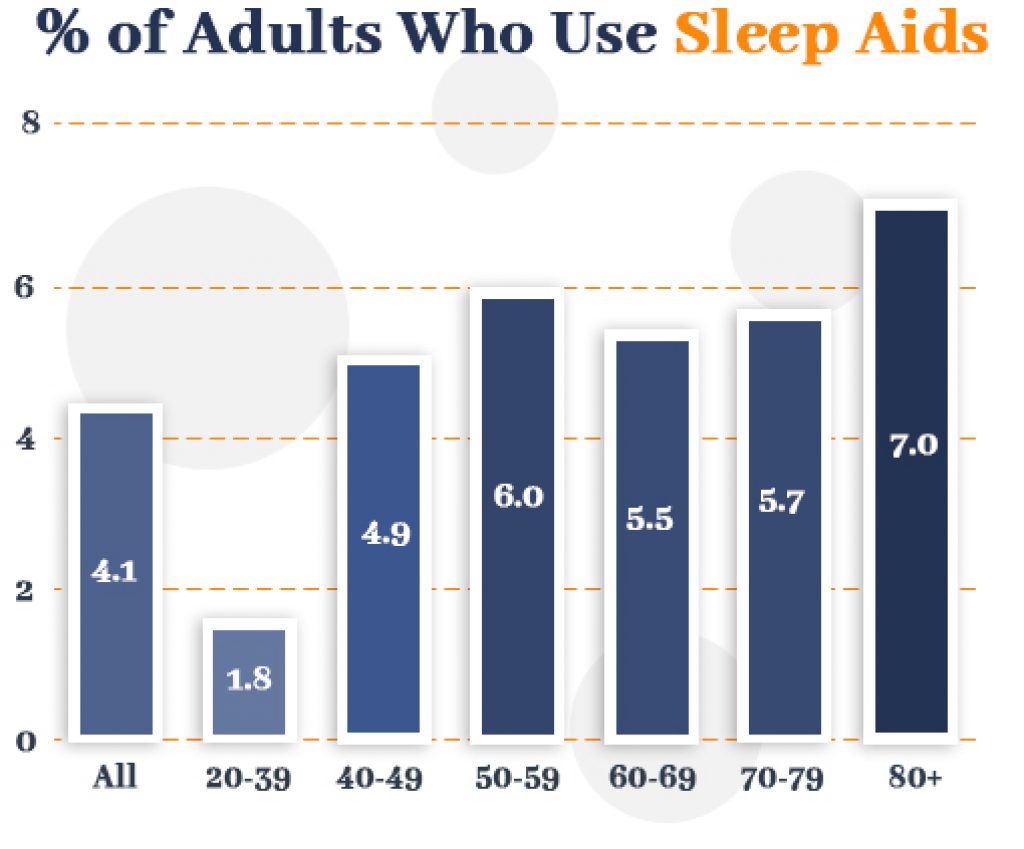
Over 4% of U.S. adults (age 20 and over) said they took some sort of medication or sleep aid in the last 30 days.
[32] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Explore the best sleep aid supplements.
8% of older adults take prescription medication to help them sleep.
[33] University of Michigan Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation
Explore our picks for the best natural sleep aid.
There are over 2500 sleep centers in the United States accredited by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine.
Over 16% of adults using some form of sleep aids have reported a physician’s diagnosis of a sleep disorder, which is 5 times higher than in those who did not report such diagnosis.
[32] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Sleep medication use was higher among women (5%) compared to men (3.1%).
The frequency of sleep medication use is associated with a higher mortality rate.
China is the most “sleep-medicated” country in the world.
People who take hypnotics for sleep have an increased risk of developing cancer.
The CPAP device market is valued at $4.3 billion and growing 7.2% a year.
Technology and Sleep
Spring mattresses are the most popular type of bed.
Check out our picks for the best innerspring mattress.
Over 28% of surveyed adults say they use their mobile phones to track their sleep.
Those who reported having an “excellent” diet were more likely to use a sleep tracker.
People who use their phones to check other health functions were more likely to track their sleep.
The global Smart Mattress market size annual growth is 64.13% and is expect to reach over $8 billion by 2028.
North America is expected to account for 54% of the Sleep Tracking device market share by 2024.
30-50% of people surveyed say they believe sleep tracking apps will increase sleep pattern and hygiene awareness, influence their sleeping habits, and motivate them to seek help for better rest when needed.
[43] National Library of Medicine
View our picks for the best sleep trackers.

Julia Forbes
Lead Product Tester
About Author
Julia is the Lead Reviewer at Sleep Advisor, specializing in testing out mattresses and sleep accessories – she’s in the right line of work, because she loves to sleep.
Stomach Sleeper
Sources and References:
[1] Stress and Sleep, American Psychology Association
[2] Physiology, Sleep Stages, National Library of Medicine
[3] Effects of thermal environment on sleep and circadian rhythm, National Library of Medicine
[4] Sleep positions and nocturnal body movements based on free-living accelerometer recordings: association with demographics, lifestyle, and insomnia symptoms, Nature and Science of Sleep
[5] The Co-Occurrence of Sexsomnia, Sleep Bruxism and Other Sleep Disorders, MDPI – Journal of Clinical Medicine
[6] In U.S., 40% Get Less Than Recommended Amount of Sleep, Gallup News
[7] Age 40 is when busy Americans get the least sleep, Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University
[8] Lack of Sleep Costs U.S. About $411 Billion in Lost Productivity, Study Finds, Fortune Magazine
[9] Are you getting enough sleep?, Harvard Health
[10] Teenagers and sleep, Better Health
[11] How Sleep Affects Your Health, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
[12] Assessment of Physician Sleep and Wellness, Burnout, and Clinically Significant Medical Errors, JAMA Network
[13] How much sleep do I need?, CDC
[14] Sleep Disorders and Sleep Deprivation, National Center for Biotechnology Information
[15] Which state has the most sleep-deprived residents in the country?, USA Today
[16] Functional and Economic Impact of Sleep Loss and Sleep-Related Disorders, National Library of Medicine
[17] Sleep, Harvard School of Public Health
[18] Common Sleep Disorders, Cleveland Clinic
[19] Snoring, Yale Medicine
[20] Drowsy Driving — 19 States and the District of Columbia, 2009–2010, CDC
[21] What Are Sleep Deprivation and Deficiency?, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
[22] What doctors wish patients knew about insomnia, American Medical Association
[23] Insomnia, Cleveland Clinic
[24] Sleep Disorders, National Alliance on Mental Illness
[25] Estimation of the global prevalence and burden of obstructive sleep apnoea: a literature-based analysis, National Library of Medicine
[26] Influence of Gender on Associations of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Symptoms with Chronic Conditions and Quality of Life, National Library of Medicine
[27] Prevalence of undiagnosed obstructive sleep apnea among adult surgical patients in an academic medical center, National Library of Medicine
[28] Obstructive sleep apnea is a common disorder in the population—a review on the epidemiology of sleep apnea, National Center for Biotechnology Information
[29] Narcolepsy, National Organization for Rare Disorders
[30] Narcolepsy Fact Sheet, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
[31] Misdiagnosis of narcolepsy, National Center for Biotechnology Information
[32] Prescription Sleep Aid Use Among Adults: United States, 2005–2010, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
[33] 1 in 3 older adults take something to help them sleep – but many aren’t talking to their doctors, University of Michigan Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation
[34] Sleep medicine in America: Infographic, American Academy of Sleep Medicine
[35] Use of Sleep Medications and Mortality: The Hordaland Health Study, National Center for Biotechnology Information
[36] The world’s largest-ever online ‘sleep census’ reveals a sleep-deprived planet, Loughborough University
[37] Hypnotics and Risk of Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies, National Library of Medicine
[38] Top 6 Things to Know About the $28 Billion Sleep Market, Market Research
[39] Examining Use of Mobile Phones for Sleep Tracking Among a National Sample in the USA, Health Communication Journal
[40] Mattress Retail in the U.S. – Statistics & Facts, Statista
[42] Smart Sleep Tracking Device Market : Global Demand Analysis & Opportunity Outlook 2024, Research Master
[43] Smartphone applications for sleep tracking: rating and perceptions about behavioral change among users, National Library of Medicine
