Let’s face it, parenting can be utterly exhausting. After twelve long hours of duct-taping bananas back together because you peeled them the “wrong” way and answering endless questions about why Santa has twelve (not eleven) reindeer, what’s the harm in letting the TV babysit for just a few minutes of peace and quiet?
Watching television before bedtime has been an activity that many parents have used to help their little ones wind down and fall asleep faster. As a child of the 80s, I frequently spent my evenings watching Full House or Saved by the Bell. With so many newer educational shows to choose from, what’s the danger in letting your kids watch TV before bed?
According to research – a lot! Let’s dive a little deeper into this controversial topic and see what science has to say about how television may impact children’s sleep habits.
A Time-Honored Tradition
Nearly a century ago, families could likely be found seated around a large radio, listening to the evening programs before bed. As technology advanced, families continued to gather together after dinner, only instead of listening to the radio, they could be found huddled together on the sofa, watching The Ed Sullivan Show or Howdy Doody on a 14-inch black and white screen.
Generations later, many parents and children still gather together in the evenings to watch a favorite program after their meal. Whether it is Nick-at-Nite or the 7 o’clock news, people spend up to 50% of pre-bedtime watching television, according to an American Time Use Survey.
As a young child, I often fell asleep to the soothing stories that sounded from a cassette player that sat on my dresser. I became accustomed to listening to these exciting tales as I drifted off, often dreaming of the adventures that I’d heard. There is something magical about being transported out of your own boring life into a world beyond your imagination, where dreams really do come true.
Many children are used to being read to as part of their bedtime routine, a practice that is important for literacy and early learning. Reading together can also be a time of reconnection for families who may be apart for many hours during the day. Unfortunately, while watching TV as a family is technically time spent together, the lack of face-to-face interaction disqualifies this activity as a bonding experience.
Get More Info: Sleeping With Television On
What Does the Science Say About Watching TV Before Bed?
I watched TV before bed growing up and I turned out fine, so what’s the problem? It’s only for a few minutes, how bad could it be? How much is too much? If you’ve wrestled with these questions, you’re not alone.
For years, parents and the medical community alike have debated the amount of television kids should be watching, especially before bedtime. The World Health Organization’s (WHO) latest guidelines on physical activity, sleep, and sedentary behavior for children under the age of 5 states that “Sedentary screen time should be no more than 1 hour; less is better.”
Similarly, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) has recommended that this same age group should be limited to watching no more than one hour of high-quality, educational programming with their parents or care-givers. In addition, the AAP “suggests that all screens be turned off 30 minutes before bedtime and that TV, computers and other screens not be allowed in children’s bedrooms.”
But why are pediatricians and sleep scientists so concerned about limiting screen time in children and what’s the big deal with letting kids watch a little TV before bed? Let’s look a little more closely at how viewing television impacts children’s health according to Science.
Delayed Sleep Cycle
One of the most common reasons parents allow their children to watch television in the evening is to help them relax and (hopefully) fall asleep faster. Unfortunately, some research is pointing to the fact that the opposite may be true. In a parent completed survey of sleep habits in 207 children aged 8-17, watching television before bedtime reduced total time resting by 30 minutes.
Another study looking at sleep and TV viewing in 495 children in kindergarten through grade four found that there was a delayed onset of sleep and shorter overall rest time when children watched television before bedtime. This study also found that having a television in the child’s bedroom was the most powerful predictor of overall sleep disturbance.
While missing out on a few minutes of rest doesn’t seem like a big deal, the long-term effects of sleep disturbances in children are staggering. Kids and teens who don’t get enough rest have a greater risk of experiencing increased injuries, depression, hypertension, and even obesity. On the other hand, adequate sleep during these crucial years of development promotes mental and physical health and may lead to improved attention, behavior, memory, learning, emotional regulation and better quality of life.
Learn More: Delayed Sleep Phase Syndrome Explained
Anxiety-inducing
Many often reminisce about how life was simpler in older days when children spent more time playing outside and families raised kids in community instead of isolation. Back then, it seemed like the only thing kids had to worry about was who was going to be “it” for hide-and-seek and whether Mom was cooking that awful meatloaf recipe for dinner again. Unfortunately, as technology use and screen-time have increased in children, so has anxiety for many children.
Despite the WHO and AAP recommendations for limiting screen time to less than one hour of educational programming, children are spending hours watching TV each day, often viewing violent and disturbing images that are intended for adults only. Young children who lack the mental capacity to rationalize what they have viewed may internalize their fears and experience anxiety.
In the same study of 495 children mentioned above, watching television before bed increased anxiety, making it harder to fall asleep and causing more night-time wakings. According to another study of 153 university students, 90% reported encountering frightening media as children, producing residual anxiety that was still present at the time of measurement in more than 26% of students.
Nightmares
Almost everyone, including adults, can probably relate to having a nightmare after watching something scary. I will never forget waking up drenched in sweat following a particularly terrifying dream about a clown after watching the movie “It” for the first time…thank you, Stephen King. Unfortunately, children are much more susceptible to experiencing nightmares, especially if they watch programming right before falling asleep.
A 2011 study in the Journal of Pediatrics found that children who watched television with/without violent images just before bed had more nightmares and trouble falling and staying asleep. Another study of 100 healthy children found that those with televisions in their bedrooms had significantly more reports of sleep terrors and nightmares. Watching TV in the evening also increased disturbances more than viewing earlier in the day.
Learn More: How to Ease Nightmare in Toddlers
Blue Light
Another popular subject that has recently received a lot of media attention is blue light. Artificial blue light emitted from screens and other electronics has been shown to harm the circadian rhythm, the body’s internal clock. This artificial light can delay the release of the sleep-inducing hormone, melatonin, increasing alertness and disrupting sleep cycles.
Typically, the pineal gland begins to release melatonin a couple of hours before bedtime in response to decreased light. When people are exposed to blue light from electronic screens, fluorescent bulbs, or LED lights, this process is delayed. Blue light exposure in the evening hours could make it more difficult to fall asleep, decrease REM sleep, and cause people to wake up still feeling tired despite achieving adequate hours of rest.
One of the ways to protect your eyes from the blue light exposure are the blue light blocking glasses.
Find Out More: How Technology Impacts Your Sleep
Different Effects of TV on Different Ages
Just as different screen time recommendations have been given for children based on their ages, the impact of television viewing before bed can vary by age group too.

Toddlers & Preschoolers
A quick scroll through Netflix would show you that one of the fastest-growing sectors of programming is shows designed for little ones under the age of four. What’s not to love about these adorable shows that feature fun songs teaching kids about numbers, shapes, and letters? Unfortunately, many parents (myself included) have mistakenly viewed this as permission of sorts, justifying additional screen time as “learning time.”
Educational or not, little if any benefit has ever been found in young children watching TV. The WHO recommends that children in this age bracket get between 10-14 hours of rest a day for proper growth and development. Kids in these early years should be watching no more than one hour of TV a day, but even this minimal amount may have negative effects.
A study looking at screen time in toddlers aged 24 months and younger found that for every hour of screen time, total sleep time was reduced by almost half-an-hour! Another study involving over 450 preschoolers found that those who watched less than one hour of TV per day got 22 more minutes of sleep at night, totaling 2.5 hours more hours per week than those who watched more than one hour daily. Preschoolers without TVs in their bedrooms also slept 30 minutes more at night than those with a TV in their bedroom.
School-aged Children
Once kids hit the school-aged years, their total number of hours spent sleeping often starts to decrease while their screen time subsequently increases. Oftentimes, kids in this age range spend time watching television in the mornings before school, may be exposed to television as part of their school day, and frequently spend additional time watching TV in the evenings before bed.
Similar to the studies done on preschoolers, research has found a direct correlation between the length of time spent watching television and decreased sleep duration in school-aged children. In addition, they found that “violent scenes in animated features may also lead to impulsive aggressive behaviors among children younger than 8 years because they may be unable to distinguish between real life and fantasy.”
Teens
Of all kids, teens spend the greatest amount of time watching television, movies, or video games on top of the excessive time they spend on computers, tablets, and phones. Some statistics show that adolescents ages 8-18 spend as many as 9 hours a day using entertainment media, with numbers rising every year.
Greater media use has been associated with less time spent sleeping at night (causing teens to sleep in later in the morning) and increased fatigue. A study of 55 adolescents found that media use after bedtime was correlated with later onset and decreased sleep efficiency. According to the 2006 Sleep in America Poll, teens who have set rules about TV time sleep on average half-an-hour more per night.
Learn More: Beds for Teenagers
On the Other Hand…
With the increased use of media and research reporting that 50-90% of children may not be getting the rest they need, how can we not point the finger at media? While studies demonstrating the negative effects of watching TV in kids are abundant, some new research suggests that maybe television isn’t the villain we’ve made it out to be.
A recent study at the University of Oxford found very little association between screen time and sleep disturbance in children. Professor Andrew Przybylski, the author of this study, stated that “Every hour of screen time was related to 3 to 8 fewer minutes of sleep a night.”
While these numbers were less than in other similar research, this study did find that children who followed the AAP guidelines on screen time reported between 20 and 26 more minutes of sleep at night.
Possible Alternative Bedtime Rituals
If you’re concerned about your children watching television before bed, there are lots of great alternatives that may even improve bedtime for your little ones. While you may face some opposition if your kids have become accustomed to TV time in the evening, gradually reducing the amount of time and spinning the change in a positive light may help to ease some of their dissent.
You may have to play around with evening activities until you find a routine that works for your family, but these 8 bedtime rituals should help to get you started!
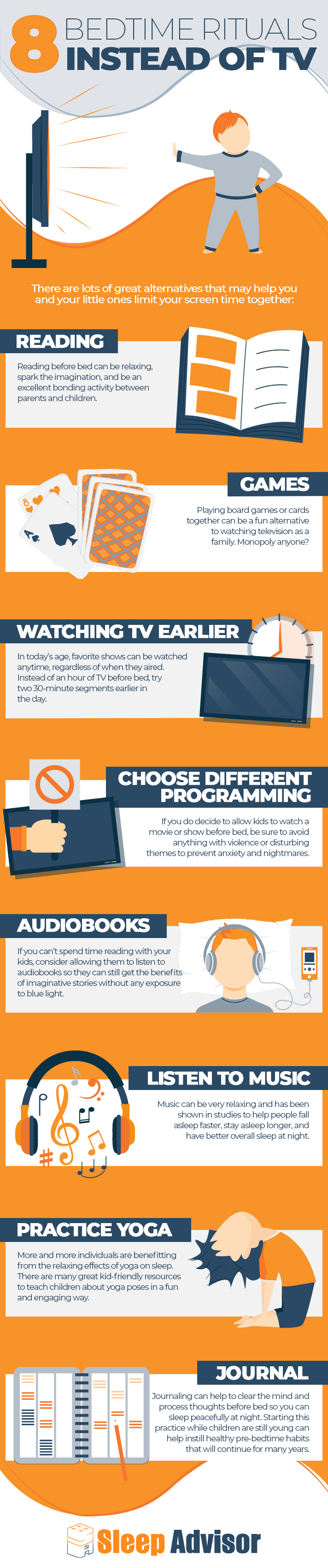
8 Bedtime Rituals Instead of TV
- 1. Reading – Reading before bed can be relaxing, spark the imagination, and be an excellent bonding activity between parents and children.
- 2. Games – Playing board games or cards together can be a fun alternative to watching television as a family. Monopoly anyone?
- 3. Watching TV Earlier – In today’s age, favorite shows can be watched anytime, regardless of when they aired. Instead of an hour of TV before bed, try two 30-minute segments earlier in the day.
- 4. Choose Different Programming – If you do decide to allow kids to watch a movie or show before bed, be sure to avoid anything with violence or disturbing themes to prevent anxiety and nightmares.
- 5. Audiobooks – If you can’t spend time reading with your kids, consider allowing them to listen to audiobooks so they can still get the benefits of imaginative stories without any exposure to blue light.
- 6. Listening to Music – Music can be very relaxing and has been shown in studies to help people fall asleep faster, stay asleep longer, and have better overall sleep at night.
- 7. Practice Yoga – More and more individuals are benefitting from the relaxing effects of yoga on sleep. There are many great kid-friendly resources to teach children about yoga poses in a fun and engaging way.
- 8. Journal – Journaling can help to clear the mind and process thoughts before bed so you can sleep peacefully at night. Starting this practice while children are still young can help instill healthy pre-bedtime habits that will continue for many years.
Conclusion
While the jury is still out on just how detrimental watching TV before bed is in kids, we do know that it could impact the overall amount of rest kids are getting and cause anxiety or nightmares depending on what they are watching.
Sleep is extremely important for learning, memory, health, emotional regulation, and so much more. As a parent, I’m concerned enough by the research to set some new rules about watching television before bedtime in my household. While we may still enjoy the occasional movie night cuddled together on the couch, our bedtime routine will look a lot more like books, bath, and bed!

Raina Cordell
RN, RHN, Certified Health Coach
About Author
Raina Cordell is a Registered Nurse, Registered Holistic Nutritionist, and Certified Health Coach, but her true passion in life is helping others live well through her website, www.holfamily.com. Her holistic approach focuses on the whole person, honing the physical body and spiritual and emotional well-being.
Combination Sleeper
